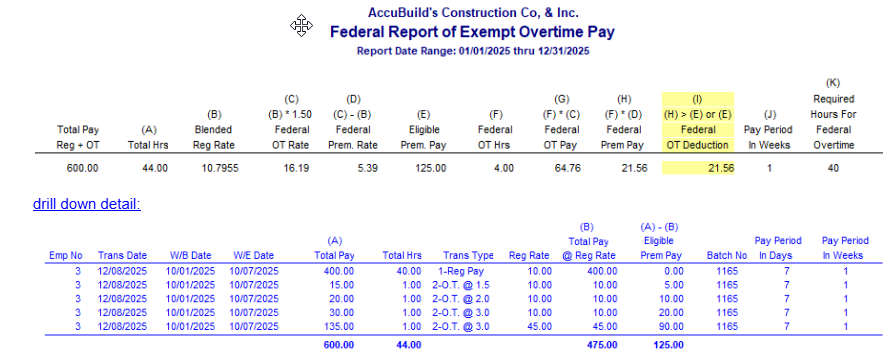
At the end of 2025, a new report was added to the MAR Report Library under the Payroll Reports section titled 'Federal Report of Exempt Overtime Pay'. This report can be used to determine the amount of Federal Overtime Pay that is eligible for deduction under the One Big Beautiful Bill Act (OBBBA) passed by the Trump Administration. The report will compute the actual amount of the overtime pay that can be deducted for each employee based on the following Federal Overtime Rules:
•Only the hours in excess of 40 hours per week are eligible for the overtime deduction.
•Only the premium pay portion calculated at time and a half is eligible for the overtime deduction.
•The Federal Overtime Rate is based on a blended regular rate computed at time and a half. This is due to the fact that construction industry payroll rates can vary for different work tasks, union rules, and federal and state project rules for prevailing wage requirements.
| Blended Reg Rate = Total Pay*** @ Reg Rate / Total Hours |
*** Transactions with Regular Pay and Overtime Pay transaction codes only.
Column (I) - Federal OT Deduction
This column (highlighted in yellow) represents the amount of Exempt Overtime Pay that will be included on the employee’s W2 that is generated from Aatrix. The Aatrix Software allows for these amounts to be edited before finalizing the W2 process in case you need to make any adjustments:
Non Weekly Payroll WARNING:
This report is designed for computing Federal Overtime on a weekly payroll basis. If your payroll is not created for a weekly basis, you will need to review the report totals because any entries that are not based on a 40 hour weekly (7 day) period will be flagged with a warning.
Non weekly payroll entries will be computed using the number of weeks in the pay period times 40 hours in order to be consistent with the Federal Rules for qualified weekly overtime. This report cannot determine how to separate multiple weeks of pay on a single paycheck into individual weeks.
If you need to compute these totals manually, set up this report as an MAR Dataview in Accubuild. The dataview will allow you to access the FEDOTDRILLDOWNTRANS table to get a detail of the time card transactions by employee number that you can export to excel to help in computing your overtime amounts. This datapipe will provide several columns that you can use for computing your totals and you can group your totals in the spreadsheet by employee number (e_no), week ending date (we_date) and the pay period in weeks (PayPeriodInWeeks):
•Hours - hours worked for the time card entry
•RegRate - regular rate of pay for the time card entry. For overtime transactions, the trans_desc field on overtime transactions will indicate the factor applied to the regular rate to obtain the transaction Amount.
•Amount - Amount paid for the Hours worked for regular pay and overtime pay transactions.
•AmountAtRegRate - This is a computed amount of the total Hours (both regular and overtime) multiplied by the RegRate
•EligiblePremiumPay - This is a computed amount that represents the overtime premium amount and is computed using the difference between the Amount (actual paid) and the computed AmountAtRegRate. The Federal OT Deduction amount should never exceed this amount.
Calculation Example:
The following is an example of a manual calculation method for computing the overtime pay exemption amount based on AI research. This is just an example, please be sure to consult with your CPA firm regarding the method you use for reporting your overtime pay exemption amounts. Remember that the Federal Rules for overtime pay are different from any state, union, or prevailing wage requirements.
Full Example Scenario: Multiple Pay Rates + Overtime
Employee: Hourly, non-exempt
Workweek: 7 consecutive days (FLSA standard)
Hours worked in week:
32 hours at $20/hr
16 hours at $25/hr
Total = 48 hours → 8 overtime hours (FLSA)
NOTE: Even though some hours are paid at different rates, the regular rate for overtime purposes must be blended under FLSA unless the employer uses the authorized "rate-in-effect" method (which has strict rules). The most common and safest method is weighted average (blended rate).
STEP 1 — Calculate Total Straight-Time Earnings
Hours Rate Earnings
32 hrs $20 $ 640
16 hrs $25 $ 400
Total $1,040
STEP 2 — Compute FLSA Regular Rate (Blended)
FLSA Regular Rate = Total straight-time earnings ÷ total hours worked
= $1,040 ÷ 48 = $21.67/hr (This is the correct regular rate for overtime.)
STEP 3 — Compute FLSA Overtime Rate
FLSA OT rate = Regular rate × 1.5
= $21.67 × 1.5 = $32.50/hr
STEP 4 — Compute the FLSA Overtime Premium Portion
Only the premium portion is deductible under OBBBA.
Premium = OT rate − Regular rate
= $32.50 - $21.67 = $10.83/hr
STEP 5 — Compute Qualified Overtime Compensation (QOC)
Only premium × number of OT hours qualifies.
= $10.83 × 8 hrs
= $86.64 qualified overtime deduction for this week. This is the amount the employee may deduct from taxable income for 2025 (subject to annual caps).
Helpful Links:
Below are some helpful government links for further information on the overtime pay exemptions for employees:
•IRS Guidance on OBBB Act Provisions: The IRS provides official details on the tax deduction for qualified overtime compensation through the IRS One, Big, Beautiful Bill provisions page.
•IRS Notice 2025-69: This notice provides guidance for individuals on how to calculate their qualified overtime deduction for the 2025 tax year, especially if employers do not provide separate reporting on Form W-2. It is available on the IRS website.
•IRS Penalty Relief Guidance (Notice 2025-62): This document details the penalty relief for employers for the 2025 tax year regarding the new reporting requirements. It is available on the IRS website.
•DOL FLSA Overtime Pay Fact Sheet: For the core FLSA overtime regulations (which determine when overtime must be paid, separate from the OBBB tax deduction), refer to the U.S. Department of Labor's Overtime Pay page and Fact Sheet #23: Overtime Pay Requirements of the FLSA.